Embark on a captivating journey into the Earth’s interior with our Earth’s Interior Structure Webquest Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of our planet’s intricate layers, revealing the fascinating composition and dynamics that shape our home.
Delve into the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core, discovering their unique characteristics and the profound role they play in shaping the Earth’s surface, driving plate tectonics, and generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
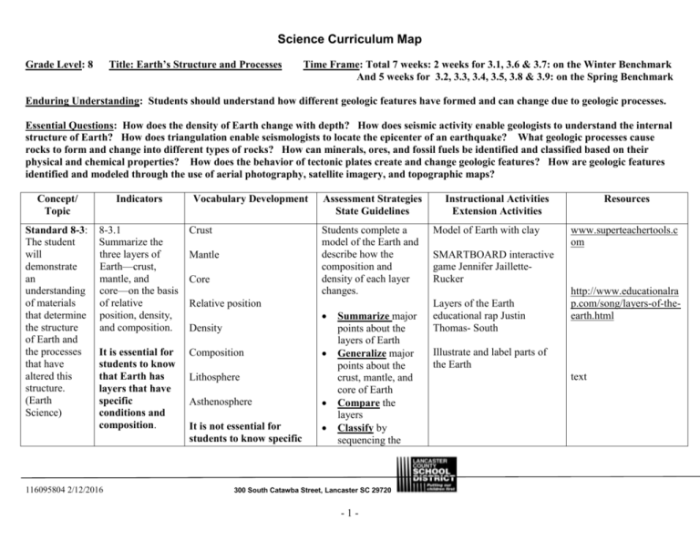
Earth’s Interior Structure: Earth’s Interior Structure Webquest Answer Key
The Earth’s interior is divided into layers based on their composition and physical properties. These layers, from the surface to the center, are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
The Earth’s interior is not directly observable, but scientists use various techniques, such as seismic waves, to study its structure and composition.
Crust
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, ranging in thickness from 5 to 70 kilometers. It is composed of solid rock and is divided into two main types: continental crust and oceanic crust.
- Continental crust is thicker and less dense than oceanic crust, with an average thickness of 35 kilometers.
- Oceanic crust is thinner and denser than continental crust, with an average thickness of 7 kilometers.
The crust plays a crucial role in plate tectonics, as it is the layer that is broken and moved by the movement of tectonic plates.
Mantle, Earth’s interior structure webquest answer key
The mantle is the layer beneath the crust, extending to a depth of about 2,900 kilometers. It is composed of solid rock that is hotter and denser than the crust.
The mantle is divided into two layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
- The upper mantle is more viscous than the lower mantle and is where most earthquakes occur.
- The lower mantle is more rigid than the upper mantle and is believed to be convecting, which drives plate tectonics.
Outer Core
The outer core is the layer beneath the mantle, extending to a depth of about 5,150 kilometers. It is composed of liquid iron and nickel.
The outer core is believed to be responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field, which protects the planet from harmful solar radiation.
Inner Core
The inner core is the innermost layer of the Earth, extending to a depth of about 6,371 kilometers. It is composed of solid iron and nickel.
The inner core is under extreme pressure and temperature, and it is believed to be rotating at a slightly different rate than the rest of the Earth.
Q&A
What is the Earth’s crust made of?
The Earth’s crust is primarily composed of igneous and metamorphic rocks, formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock or the transformation of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
How thick is the Earth’s mantle?
The Earth’s mantle extends from the base of the crust to a depth of approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles), making it the thickest layer of the Earth.
What is the role of the outer core in the Earth’s magnetic field?
The outer core is composed of molten iron and nickel, and its movement generates electric currents that create the Earth’s magnetic field, which protects the planet from harmful solar radiation.