Enzymes and cellular regulation POGIL is an engaging and interactive learning experience that helps students explore the fascinating world of enzymes and their critical role in regulating cellular processes. By delving into the intricacies of enzyme structure, function, and regulation, this POGIL activity empowers students to unravel the secrets of cellular life.
Enzymes, the workhorses of cells, catalyze biochemical reactions that drive countless processes essential for life. Their intricate structure and exquisite specificity enable them to orchestrate a vast array of chemical transformations, from nutrient breakdown to DNA replication. Understanding how enzymes function and how they are regulated is paramount to comprehending the intricate workings of cells.
Enzyme Structure and Function
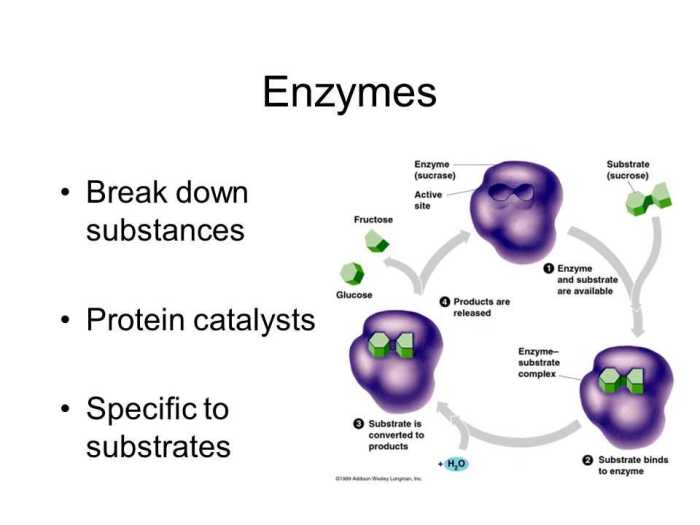
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. They play a crucial role in cellular metabolism, enabling biochemical reactions to occur at rates compatible with life.
Basic Structure and Components of Enzymes
- Enzymes are typically composed of one or more polypeptide chains folded into a specific three-dimensional structure.
- The active site is a specific region of the enzyme where the substrate binds and the catalytic reaction takes place.
- The active site contains specific amino acid residues that interact with the substrate and facilitate the chemical reaction.
Role of Active Sites in Enzyme Function
- Active sites provide a specific environment for the substrate, optimizing the interactions and orientation necessary for catalysis.
- The amino acid residues in the active site form bonds with the substrate, lowering the activation energy and facilitating the reaction.
- Enzymes are highly specific for their substrates due to the unique shape and chemical properties of their active sites.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
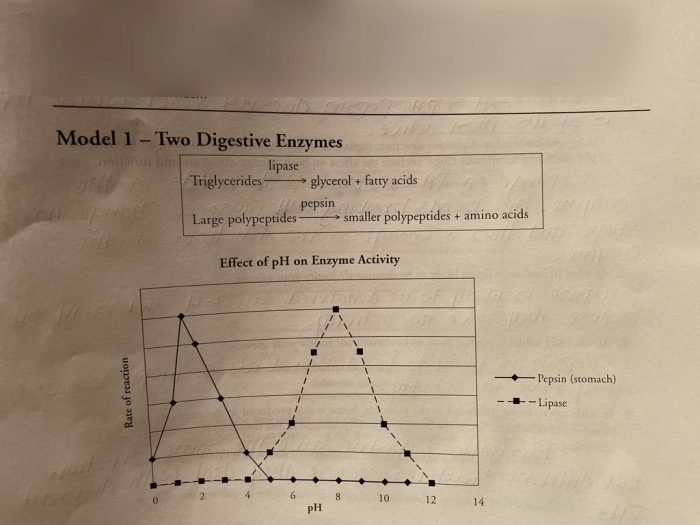
- pH:Enzymes have an optimal pH range at which they exhibit maximum activity. Deviations from this range can alter the ionization states of the amino acid residues in the active site, affecting substrate binding and catalysis.
- Temperature:Enzymes have an optimal temperature range for activity. Extreme temperatures can denature the enzyme, disrupting its structure and catalytic function.
Enzyme Regulation

Enzyme activity is tightly regulated to ensure proper cellular function. Various mechanisms regulate enzyme activity, including:
Feedback Inhibition
- Occurs when the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits the activity of an enzyme earlier in the pathway.
- Helps prevent overproduction of the end product and maintain metabolic balance.
Allosteric Regulation
- Involves the binding of a molecule (allosteric effector) to a site on the enzyme other than the active site.
- Can either activate or inhibit enzyme activity by altering the enzyme’s conformation.
Enzyme Inhibitors and Activators
- Inhibitorsbind to enzymes and reduce their activity.
- Activatorsbind to enzymes and increase their activity.
- Both inhibitors and activators can be used to control enzyme activity in cells.
Importance of Enzyme Regulation in Cellular Metabolism
- Ensures that metabolic pathways operate efficiently and in a coordinated manner.
- Allows cells to respond to changes in the environment and adjust their metabolism accordingly.
Cellular Regulation
Enzymes play a crucial role in cellular processes, including:
Metabolism
- Enzymes catalyze the chemical reactions involved in energy production, nutrient breakdown, and waste removal.
- Regulating enzyme activity allows cells to control metabolic processes and maintain energy balance.
Signal Transduction
- Enzymes transmit signals within cells by modifying signaling molecules.
- Regulating enzyme activity allows cells to respond to external stimuli and coordinate cellular responses.
Homeostasis
- Enzymes contribute to maintaining cellular homeostasis by regulating metabolic processes and signal transduction pathways.
- Dysregulation of enzyme activity can lead to cellular dysfunction and disease.
POGIL Activity
The Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) activity is a student-centered learning approach that guides students through a series of inquiry-based activities.
POGIL Activity on Enzyme Regulation
- Students investigate the effects of pH and temperature on enzyme activity.
- They design experiments, collect data, and analyze results to understand how enzymes are regulated.
Benefits of POGIL in the Classroom
- Encourages active learning and student engagement.
- Develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Promotes understanding of enzyme regulation and its importance in cellular processes.
Challenges of POGIL
- Can be time-consuming.
- Requires students to be actively involved and prepared.
Expert Answers: Enzymes And Cellular Regulation Pogil
What is the role of enzymes in cellular regulation?
Enzymes act as gatekeepers of cellular processes, controlling the rate and direction of biochemical reactions. They enable cells to respond to internal and external cues, maintaining cellular homeostasis and coordinating complex biological functions.
How does enzyme regulation contribute to cellular metabolism?
Enzyme regulation ensures that metabolic pathways operate efficiently and in a coordinated manner. It allows cells to fine-tune their metabolism based on nutrient availability, energy demands, and environmental cues, optimizing energy production and resource allocation.